We often encounter customers ask to offer them best price of multimode cable patch cord, but no further details. But however, what is the best?
In transmission and cable access networks, the main types of fiber: G.652, G.654 and G.657 are all single-mode fibers. Multimode fiber is mainly used in short distance communication, such as interconnection between devices in data centers, inner buildings or campus or other scenarios.
As we know, OM stands for optical multimode, muliti mode fiber is OM fiber, mulitmode fiber types are OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5. The physical difference of 5 types of multimode fiber are the fiber core diameter: OM1 fiber is 62.5micron, OM2 fiber to OM5 fiber are 50micron. The larger core means that multiple modes of light travel down the core at the same time, that is “multimode”. The main difference between om3 om4 om5 are the mode bandwidth, support for SWDM, etc.

Mode bandwidth
Mode bandwidth is an important indicator that reflects the bandwidth capability of multi mode optical fiber. It can be simply understood as: the product of the highest frequency of the signal transmitted in the optical fiber and its transmission length. For example, at a wavelength of 850nm, the minimum mode bandwidth of a certain optical fiber is 200MHz·km, which means that when the optical fiber is lkm long, it can transmit a signal with a maximum frequency of 200MHz; and when the length is 500m, it can transmit a maximum signal of 400MHz (200MHz×lkm/0.5km=400MHz).
The mode bandwidth of multi-mode fiber is related to the wavelength of the channel. The minimum mode bandwidths of OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5 fibers at 850nm and 953nm are shown in the table below.
| Fiber type | OM1 | OM2 | OM3 | OM4 | OM5 |
| Minimum mode bandwidth under full injection condition at 850nm (MHz.km) | 200 | 500 | 1500 | 3500 | 3500 |
| Minimum mode bandwidth under full injection condition at 953nm | No request | No request | No request | No request | 1820 |
| Minimum effective mode bandwidth at 850nm (MHz.km) | Undefined | Undefined | 2000 | 4700 | 4700 |
| Minimum effective mode bandwidth at 953nm (MHz.km) | No request | No request | No request | No request | 2470 |
There is generally no difference between the minimum modal bandwidth of OM4 and OM5 at 850nm. The difference lies in the support of SWDM.
Differences in transmission rate and distance
Multimode fiber is capable of transmitting over different distance ranges at different data rates, so you can choose the most suitable one for your application.
| Fiber Mode | Fast Ethernet | 1G Ethernet | 10G Ethernet | 40G Ethernet | 100G Ethernet |
| OM1 | 2000Mts | 275Mts | 33Mts | / | / |
| OM2 | 2000Mts | 550Mts | 82Mts | / | / |
| OM3 | 2000Mts | 550Mts | 300Mts | 100Mts | 100Mts |
| OM4 | 2000Mts | 550Mts | 550Mts | 150Mts | 150Mts |
| OM5 | / | / | 550Mts | 440Mts | 150Mts |
Table: multimode fiber distance chart
Support for SWDM
In single mode transmission systems, optical transceivers with a rate of 100G and above all use WDM technology. For example, 100G ER4 (40km) optical modules generally use LWDM (fine wavelength division multiplexing).

In order to improve the transmission rate of a single fiber, multi mode fiber also proposed a WDM solution, namely SWDM. SWDM is short-wave wavelength division multiplexing. The working wavelength used starts from 850 nm and increases by one wavelength every 30 nm, namely: 880nm, 910nm and 940nm. The multi-mode fiber that supports SDWM is OM5, which is also called broadband multimode fiber. This does not mean that OM1 to OM4 fibers do not support SWDM, but that there are no requirements for the optical fiber indicators at the corresponding wavelengths of SWDM.

Maximum transmission distance
The maximum transmission distance of multimode fiber is mainly related to the mode bandwidth of the optical fiber and the type of optical module. The maximum transmission distances of optical modules with different rates are shown in the table below (the transmission distances of OM3 and OM4 under SWDM from FS, and other transmission distances are from the official website of YOFC).
| Optical moudle type | multimode fiber max distance (m) | |||
| OM2 | OM3 | OM4 | OM5 | |
| 1000BASE-SR | 750 | 1000 | 1100 | 1100 |
| 10GBASE-SR | 150 | 300 | 550 | 550 |
| 40GBASE-SR4,100GBASE-SR10 | 140 | 170 | 200 | |
| 40GB/S SWDM4 | 240 | 350 | 440 | |
| 100GB/S SWDM4 | 75 | 100 | 150 | |
Note:optical module are MPO/MTP interface, single fiber transmission rate 10G | ||||
Fiber core diameter, light source
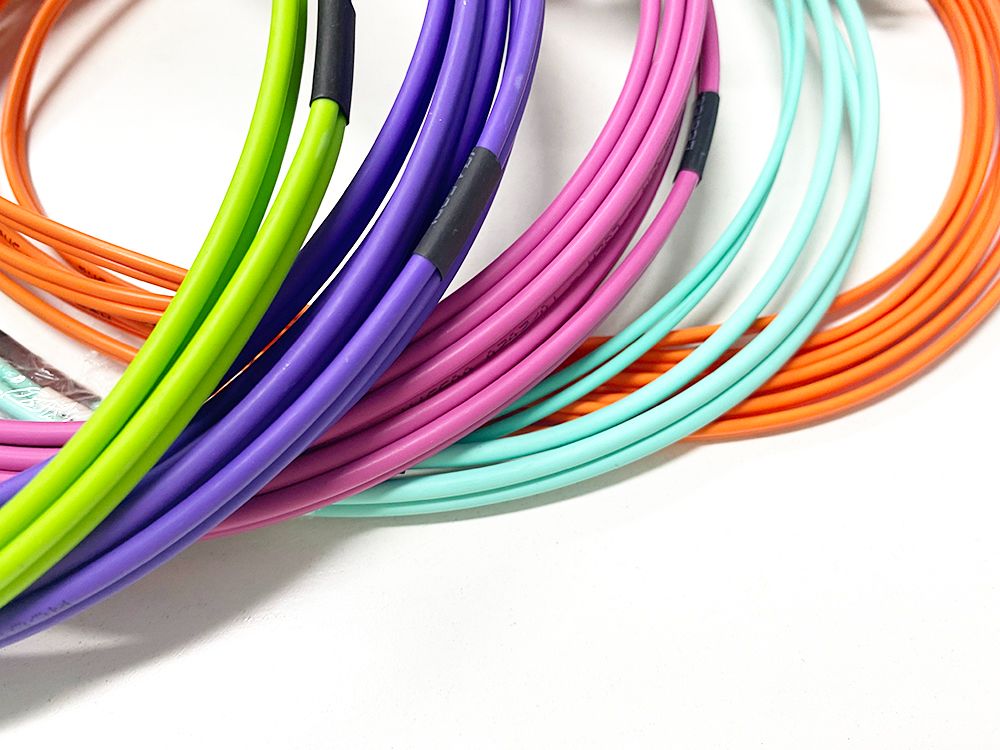
OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5 fibers have different core diameters, light source types, and patch cord jacket color.
Generally, the larger the core diameter of the fiber, the easier it is to couple, but the smaller the mode bandwidth. There are two types of core diameters for OM1 and OM2: 50um and 62.5um, and the core diameters of OM3, OM4 and OM5 are all 50um.
The light sources of OM1 and OM2 mainly use LEDs, while the light sources of OM3, OM4 and OM5 mainly use VCSELs (vertical cavity surface emitting lasers).
To distinguish multimode fiber types, patch cord jacket for multimode fiber color OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5 are also different: OM1/OM2 is orange, OM3/OM4 is aqua blue (some manufacturers use violet as the jacket of OM4 patch cords), and OM5 is light green.
Conclusion
OM1 and OM2 fibers have gradually withdrawn from the market because they cannot support high-speed communications well. Although OM5 fiber can better support SWDM, the high-speed optical module adopts the MPO/MTP solution (MPO/MTP is a multi-core fiber interface) which is more economical than the SWDM solution. Therefore, the most widely used multimode fibers are still OM3 and OM4. It is recommended to use OM4 fiber for new wiring in data centers. If you are not sensitive to investment or the rate requirement for interconnection between devices is high, you can also use OM5 fiber.
At present, except for data centers, the optical fiber for interconnection of equipment in other telecommunications rooms still uses single mode fiber. Although single-mode fiber is cheaper than multi-mode, the price of optical modules with the same rate is about twice that of multi-mode. If multi-mode fiber is also used for interconnection of equipment in the core room, it may save a lot of investment.
FAQ
Which is better OM3 or OM4?
If only on technical indicators, OM4 is better. Because OM4 bandwidth is 4700 MHz·km compared to 2000 MHz·km for OM3. This means that OM4 can transmit more information within the same distance. Meanwhile, OM4 transmission distance are longer at the same Ethernet, OM4 is 550meters compared to 300meters for OM3 in 10G, OM4 is 150meters compared to 100meters in 40G/100G.
Can I use OM4 instead of OM3?
Yes, OM4 is compatible with OM3 and technical parameters are better than OM3, but if your budget limit, suggest to use OM3 still, no matter for patch cords, backbone trunk cables or patch panels, all can connect well and vice versa.
What wavelength is multimode fiber?
Mulit mode fiber wavelength is most of time 850nm, 1300nm, but now OM5 WBMMF (Wide Band Multimode Fiber) is specially designed to specifically handle high-speed data center applications with using two fibers to transmit from 40GBs up to 100GBs and is powered by shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM). This multiplexing design allows OM5 to operate in the 850nm to 950nm range with just one pair of parallel fibers.
Why multimode fiber is not widely used in telecommunication?
Though multimode now used a lot, but during long term distance transmission, single mode is more useful. Due to multimode can maximum 550meters, if any longer than around 914 meters results in distortion of data and unclear transmission. Even in fast ethernet, it can only transmit 2km at 100Mb/s. But single mode fiber can be 20km 60 km 80km or even longer transmission. Furthermore, mulitimode fiber optic cable is more expensive than single mode fiber optic cable, so in truck cable wiring like outdoor cables, or fiber end termination side like FTTH, multimode cable is not used so much.
Can multimode fiber be used as single mode?
No, because of the large dispersion and loss of multimode fiber, optical signal cannot be transmitted over a long distance on multimode fiber.
Due to its high capacity and reliability, multimode optical fiber is usually used for backbone applications in buildings. In general, MM optical cable is still the most cost-effective choice for enterprises and data center applications within the range of 500-600 meters.
However, this does not mean that we can replace single-mode optical fiber with multimode optical cable. As for the choice of single-mode optical fiber patch cord or multimode patch cord, it depends entirely on the application, transmission distance and coverage you need. Total budget allowed.
What are the difference, om3-150 vs om3-300 ?
In China, there are 2 types of OM3 fiber, namely OM3-150 and OM3-300. OM3-150 fiber can transmit 150meters longest in 10 Gigabit Ethernet. OM3-300 is 300meters in 10 Gigabit Ethernet, so if customer need patch cord is less than 150meters, factory may use OM3-150 fiber instead, so the cost is cheaper.
What is the difference between OM4 and OM5 fiber?
Both Transmission distance and Bandwidth are different. OM5 bandwidth is 28000MHz*km,OM4 is only 4700MHz*km, that means OM5 can transmit more data at the same time and same distance. Om5 transmission in 40G is 440meter longer than 150meter of OM4. At the same time, OM5 is specially designed for 850nm to 953nm SWDM wavelength. In final products, you can see that OM5 cable is lemon gree color, OM4 is purple or aqua, the same as the fiber optic connectors.
What is the best multimode fiber?
It depends, please refer to above technical table with the project application requirements and budget of your company, the lowest, the reasonable, the best.
Under the demand of high-speed network applications, multimode optical fiber is developing towards low loss, high bandwidth and multi-wavelength multiplexing.
Nowadays, OM1 and OM2 multimode fibers are mostly used for 1G Ethernet link connection in server rooms, OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers are mostly used for 10G/40G data center fiber cabling, and OM5 multimode fibers are suitable for 40/100G high-speed Ethernet link transmission.
Compared with OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4 multimode fiber, OM5 multimode fiber has high scalability and flexibility, and can support higher speed network transmission with fewer cores, and its cost and power consumption are much lower than single-mode fiber. It can be seen that OM5 multimode fiber has the potential to be widely used in 100G/400G/1T ultra-large data centers in the future.